遇见Vue.js
- 关键词:Vue.js – 读书笔记
一、基本理论基础
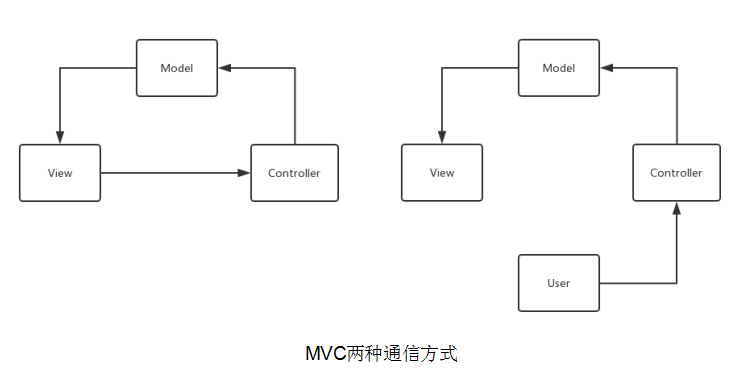
MVC
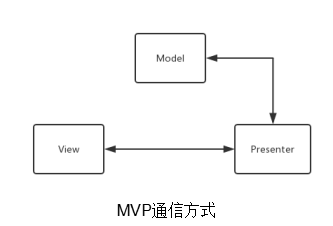
MVP
MVVM
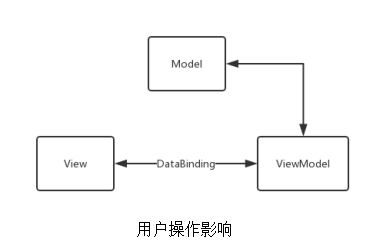
View的变化会自动更新到ViewModel,ViewModel的变化也会自动同步到View显示。
<div id="didi-navigator">
<ul>
<li v-for="tab in tabs">
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#didi-navigator',
data:{
tabs: [
{text: '巴士'},
{text: '快车'}
]
}
})
</script>
1.Vue.js的总览
Vue.js不是一个框架–它是只是聚焦视图层,是一个构建数据驱动的Web界面的库(数据绑定和灵活的组件库)。
数据绑定和组件化
//假设数据
var object = {
message: 'Hello World!'
}
//DOM
<div id="example">
</div>
//我们可以这样
new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: object
})
======================
//假设数据
var object1 = {
message: 'Hello World!'
}
var object2 = {
message: 'Hello World!'
}
//我们可以组件化
var Example = Vue.extend({
template: '<div></div>',
data: function () {
return {
message: 'Hello Vue.js!'
}
}
})
// 将该组件注册为 <example> 标签
Vue.component('example', Example)
模块化
<!-- MyComponent.vue -->
<!-- css -->
<style>
.message {
color: red;
}
</style>
<!-- template -->
<template>
<div class="message"></div>
</template>
<!-- js -->
<script>
export default {
props: ['message'],
created() {
console.log('MyComponent created!')
}
}
</script>
路由
个人感觉vue-router烦的问题是组件之间的数据交互,rootRouter的数据很难向其他组件传递.
/**
*解决方法
**/
var app = Vue.extend({
data:function(){
return {
data:'',
};
},
});
router.map({
'/': {
component: Vue.extend({
mixins: [calendar.mixin],
data:function(){
return {
data:data
}
}
})
},
})
router.start(app, '#app');
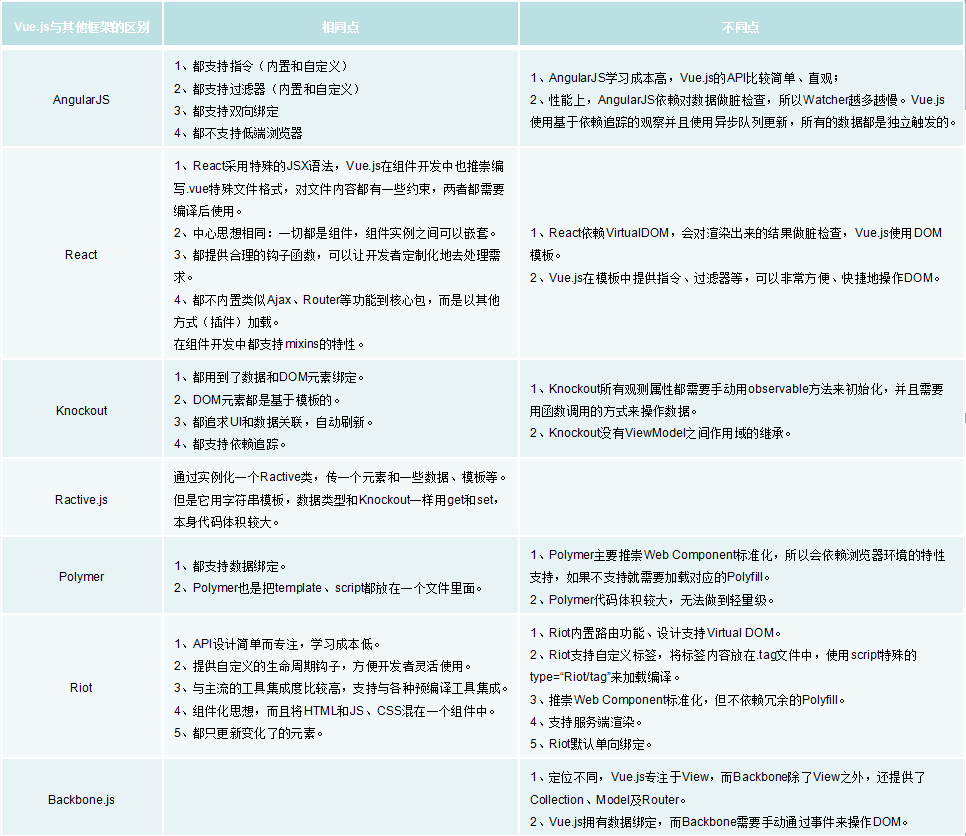
Vue.js与其他框架的区别
2.Vue.js的指令
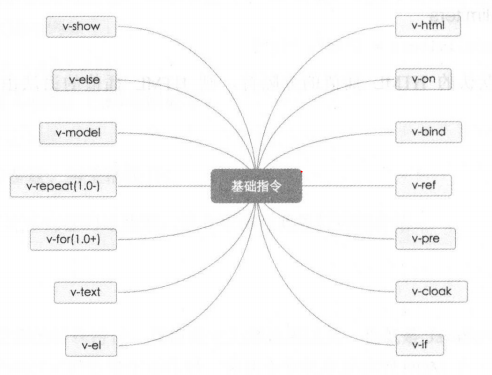
(1) v-if和v-show
v-if是根据表达式的值在DOM中生成或者移除一个元素。
v-show是根据表达式的值来显示或者隐藏HTML元素(v-show不支持template)。
一般来说,v-if有更高的切换消耗,而v-show有更高的初始渲染消耗。因此,如果需要频繁地切换,使用v-show较好;如果在运行时条件不大可能改变,使用v-if较好。
<body class="native">
<div id="example">
//生成或者移除
<p v-if="greeting">hello</p>
//style = "display: none"
<p v-show="greeting">hello</p>
</div>
</body>
<script>
var example = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
greeting: false
}
})
</script>
(2) v-else
v-else必须跟着v-if或者v-show,充当else的功能。
<body class="native">
<div id="example">
<p v-if="ok">yes</p>
<p v-else="ok">no</p>
</div>
</body>
<script>
var example = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
ok: false
}
})
</script>
//===============================
//将v-show用在组件上时,因为指令的优先级v-else会出现问题,所以不要这样做。
<custom-component v-show="condition"></custom-component>
<p v-else></p>
//我们可以用另一个v-show代替v-else
<custom-component v-show="condition"></custom-component>
<p v-show="!condition"></p>
(3) v-Model(number/lazy/debounce)
v-model是用来在input/select/text/checkbox/radio等表单控件元素上创建双向数据绑定。
根据控件类型,v-model自动选择正确的方法更新元素(有点神奇)。
<body class="native">
<form action="">
<input type="text" v-model="data.name"/>
<input type="text" v-model="data.sex"/>
//v-model指令后面可以添加多个参数
//number(将输入转换为Number类型)
//lazy(因为加了lazy属性,msg的值一直没有发生变化)
<input type="text" v-model="mgs" lazy/>
//debounce(设置一个最小的延时,在每次敲击之后延时同步输入框的值与数据)
<input type="text" v-model="mgs" debounce="50000"/>
</form>
</body>
<script>
var example = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
data:{
name: "",
sex: ""
},
msg: '内容是在change事件后才改变的'
}
})
</script>
(4) v-for
v-for指令是基于源数据重复渲染元素,$index来呈现相对应的数组索引。
使用v-for,将得到一个特殊的作用域,我们需要明确指定的props属性传递数据,否则在组件内将获取不到数据。
<body id="example">
<ul id="demo">
<li v-for="item in items" :item="item" :index="$index">
//
<li v-for="item in items" class="item-">
-
</li>
</ul>
</body>
<script>
var demo = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
items:[
parentMessage:'didi',
{mgs: '顺风车'},
{mgs: '专车'}
]
}
})
</script>
源码如下(for.js)
//parseFor
type ForParseResult = {
for: string;
alias: string;
iterator1?: string;
iterator2?: string;
};
export function parseFor (exp: string): ?ForParseResult {
const inMatch = exp.match(/([^]*?)\s+(?:in|of)\s+([^]*)/);
if (!inMatch) {
return
}
const res = {};
res.for = inMatch[2].trim();
const alias = inMatch[1].trim().replace(/^\(|\)$/g, '');
const iteratorMatch = alias.match(/,([^,\}\]]*)(?:,([^,\}\]]*))?$/);
if (iteratorMatch) {
res.alias = alias.replace(/,([^,\}\]]*)(?:,([^,\}\]]*))?$/, '')
res.iterator1 = iteratorMatch[1].trim();
if (iteratorMatch[2]) {
res.iterator2 = iteratorMatch[2].trim();
}
} else {
res.alias = alias
}
return res;
}
//=====================================================================
import { parseFor } from 'compiler/parser/index'
import { getAndRemoveAttr, addRawAttr } from 'compiler/helpers'
export function preTransformVFor (el: ASTElement, options: WeexCompilerOptions) {
const exp = getAndRemoveAttr(el, 'v-for')
if (!exp) {
return
}
const res = parseFor(exp)
if (!res) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && options.warn) {
options.warn(`Invalid v-for expression: ${exp}`)
}
return
}
const desc: Object = {
'@expression': res.for,
'@alias': res.alias
}
if (res.iterator2) {
desc['@key'] = res.iterator1;
desc['@index'] = res.iterator2
} else {
desc['@index'] = res.iterator1
}
delete el.attrsMap['v-for'];
addRawAttr(el, '[[repeat]]', desc)
}
当数组数据出现变动时如何检测呢?
源码如下(array.js)
export function def (obj: Object, key: string, val: any, enumerable?: boolean) {
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
value: val,
enumerable: !!enumerable,
writable: true,
configurable: true
})
}
//=================================================================
import { def } from '../util/index'
const arrayProto = Array.prototype;
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto);
const methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
];
/**
* Intercept mutating methods and emit events
*/
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
// cache original method
const original = arrayProto[method];
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator (...args) {
const result = original.apply(this, args);
const ob = this.__ob__;
let inserted;
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args;
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2);
break
}
if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted);
// notify change
ob.dep.notify();
return result
});
});
{
items:[
_uid: '1',
_uid: '2',
]
}
//可以这样
<div v-for="item in items" track-by="_uid"></div>
//如果没有唯一的键供追踪
<div v-for="item in items" track-by="$index"></div>
//或者给对象的键值提供一个别名
<div v-for="item in items">
:
</div>
<div v-for="(key,item) in items">
:
</div>
我们应该尽量避免直接设置数据绑定的数组元素,因为这些变化不会被Vue.js检测到,因而也不会更新视图渲染。
比如:直接用索引设置元素;修改数据的长度等
(5) v-bind
v-bind指令用于响应更新HTML特性,将一个或多个attribute,或者一个组件prop动态绑定到表达式。
<img v-bind:src = "imageSrc">
//缩写
<img :src = "imageSrc">
//绑定class或者style时
<div :class = "[classA, {classB: isB, classC: isC}]"></div>
<script>
var demo = new Vue({
el: 'example',
data:{
classA: A,
isB: false,
isC: true
}
})
</script>
//没有参数时,可以绑定到一个对象。注意,此时class和style绑定不支持数组和对象。
<div id="exampleA">
<div v-bind="{id: someProp, 'otherAttr': otherProp}"></div>
</div>
var demo = new Vue({
el: 'exampleA',
data:{
someProp: 'idName',
otherProp: 'prop'
}
})
在绑定prop时,prop必须在子组件中声明。
<my-component :prop="someThing"></my-component>
//双向绑定
<my-component :prop.sync="someThing"></my-component>
//单向绑定
<my-component :prop.once="someThing"></my-component>
//.camel-将绑定的特性名字转换为驼峰命名,只能用于普通HTML特性的绑定。
(6) v-on
用于绑定事件监听器。

//方法处理器
<button v-on:click="doThis"></button>
//内联语句
<button v-on:click="doThat('hello',$event)"></button>
//缩写
<button @click="doThis"></button>
//添加修饰符
<button @click.stop="doThis"></button>
<button @click.prevent="doThis"></button>
//串联
<button @click.stop.prevent="doThis"></button>
(7) v-ref
在父组件上注册一个子组件的索引,便于直接访问。不需要表达式,必须提供参数id。可以通过父组件的$refs对象访问子组件。
(8) 其他组件v-el、v-pre、v-cloak
v-el为DOM元素注册一个索引,方便通过所属实例的$els访问这个元素。可以用v-el:some-el设置this.$els.someEl。
<span v-el:msg>hello</span>
<span v-el:other-msg>world</span>
this.$els.mgs.textContent // hello
this.$els.otherMgs.textContent // world
v-pre跳过这个元素和它的子元素的编译过程。可以用来显示原始 Mustache 标签。跳过大量没有指令的节点会加快编译。
v-cloak这个指令保持在元素上直到关联实例结束编译。
//CSS
[v-cloak] {
display: none;
}
//html
<div v-cloak>
</div>
(9) v-text
<span v-text="msg"></span>
//等价
<span></span>
(10) v-html
不建议在网站上直接动态渲染任意HTML片段,很容易导致XSS(跨站脚本攻击)攻击。
3.自定义指令
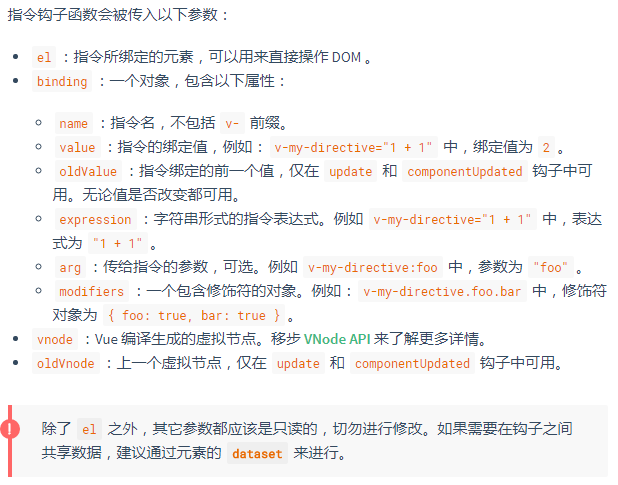
(1) 钩子函数
AngularJS提供了两个函数:compile和link,其中编译函数主要负责将作用域和DOM进行链接,链接函数用来创建可以操作DOM的指令。
Vue.js也允许注册自定义指令。自定义指令提供一种机制将数据的变化映射为DOM行为。
一个指令定义对象可以提供如下几个钩子函数(均为可选):
Vue.directive('my-directive',{
bind: function(el, binding, vnode, oldVnode){
//准备工作
//例如:添加事件处理器或只需要运行一次的高耗任务
},
inserted
//被绑定元素插入父节点时调用 (仅保证父节点存在,但不一定已被插入文档中)
update: function(newValue,oldValue){
//值更新时的工作
//也会以初始值为参数调用一次
},
componentUpdated
//指令所在组件的 VNode 及其子 VNode 全部更新后调用
unbind: function(){
//清理工作,指令与元素解绑时调用
//例如:删除bind()添加的事件监听器
}
})
//注册之后,可以这样用(添加前缀:-v):
<div v-my-directive = "someValue"></div>
//当只需要update时,可以传入一个函数替代定义对象
Vue.directive('my-directive', function(value){
//这个函数用作update()
})
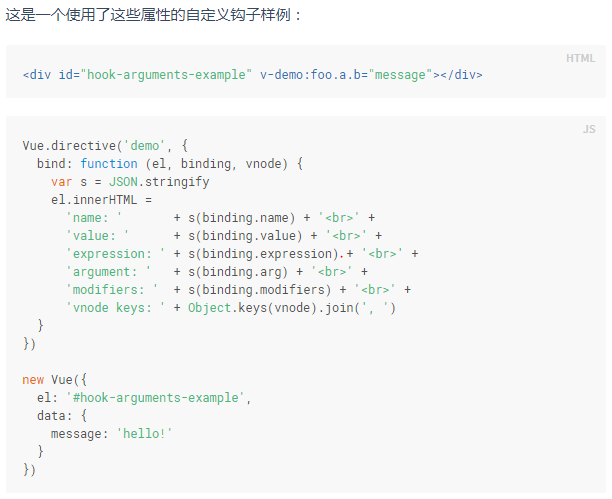
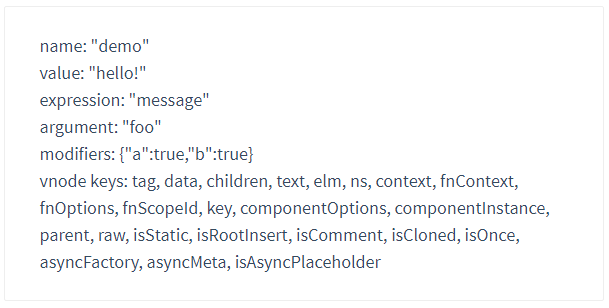
(2) 指令实例属性
所有的钩子函数,都将被复制到实际的指令对象中,在钩子内this指向这个指令对象。这个对象暴露了一些有用的属性。
(3) 对象字面量
<div id="demoA" v-model="{color: 'vhite', text: 'hello'}"></div>
<script>
Vue.directive('demoA', function (value) {
// 'white'
console.log(value.color)
// 'hello'
console.log(value.text)
})
</script>
(4) 字面修饰符
当指令使用了字面修饰符,它的值将按普通字符串处理并传递给update方法。update方法将只调用一次,因为普通字符串不能相应数据变化。
(5) 元素指令
以自定义元素的形式使用指令,而不是以属性的形式。
//自定义元素指令
<body id="demo">
<my-directive class="hello" name="hi"></my-directive>
</body>
<script>
Vue.elementDirective('my-directive', {
bind: function(){
console.log(this.el.className);
console.log(this.el.getAttribute('name'));
}
})
</script>
元素指令不能接受参数或者表达式,但是它可以读取元素的特性,从而决定它的行为。
不同于普通指令,元素指令是终结性的。这意味着,一旦vue遇到一个元素指令,它将跳出该元素及其子元素-只有该元素指令本身可以操作该元素及其子元素。
